In this article, we’ll explore a common performance issue in iOS applications: the UI hang caused by heavy computations running on the main thread. We’ll cover how to detect hangs using tools like App Hangs Detection and Instruments, simulate a UI hang scenario in a SwiftUI project, and demonstrate how to fix it effectively.
What is a UI Hang?
A UI hang occurs when the app’s user interface becomes unresponsive for an extended period. This happens when time-intensive tasks block the main thread, which is responsible for handling all UI updates and user interactions.
Apple actively discourages performing heavy computations on the main thread. Instead, developers should offload such tasks to a background thread.
The study Case : Simulating a UI Hang
Here’s a SwiftUI project that intentionally blocks the main thread with heavy computations:
import SwiftUI
struct ContentView: View {
@State private var isLoadingData = false
@State private var data: [String] = []
var body: some View {
VStack {
if isLoadingData {
Text("Loading large data...")
.font(.headline)
.padding()
ProgressView()
.scaleEffect(1.5)
} else if !data.isEmpty {
List(data, id: \.self) { item in
Text(item)
}
} else {
Text("No data loaded")
.foregroundColor(.gray)
}
Button(action: loadData) {
Text("Load Large Data")
.padding()
.foregroundColor(.white)
.background(isLoadingData ? Color.gray : Color.blue)
.cornerRadius(8)
}
.disabled(isLoadingData)
.padding()
}
.padding()
}
private func loadData() {
isLoadingData = true
// Intentionally blocking the main thread to simulate a hang
let largeData = (1...100_000).map { "Item \($0)" }
Thread.sleep(forTimeInterval: 2) // Simulate heavy computation
data = largeData
isLoadingData = false
}
}
#Preview {
ContentView()
}
Run the App
1. Launch the app on your device or simulator.
2. Press the Load Large Data button. Notice how the app becomes unresponsive.
You can confirm the hang using the App Hangs Detection tool or Instruments.
How to Detect a UI Hang
1. Detecting Hangs on a Real Device
Apple provides a built-in App Hangs Detection tool for real devices. Here’s how to enable it:
1. Connect your device to your Mac and open the Settings app.
2. Navigate to Developer > App Hangs Detection.
3. Enable the feature.
After activating this, simulate a UI hang in your app. If a hang occurs, you’ll receive a diagnostic notification showing the hang duration and stack traces.
2. Detecting Hangs Using Instruments
The Instruments tool offers precise insights into your app’s performance. To detect hangs:
1. Open Xcode and select Xcode > Open Developer Tool > Instrument.

2. Choose Time Profiler from the list.
3. Run your app on the simulator or a connected device. Make sure to choose correct simulator and correct target app installed within the simulator. Press the record button to run your app and it will launch your application, with some graphs shown.

4. Interact with your app while monitoring the Call Tree to identify methods taking excessive time.

In certain scenarios, the Hangs graph clearly indicates the presence of severe hangs. These are the performance bottlenecks that require our attention and need to be addressed. Once the hangs have been identified, we can stop the Instruments recording and dive deeper into the analysis to pinpoint the root cause.
To get a detailed view of thread activity:
• In Instruments, enable the Thread State Trace option by drag it to the Instruments list. This graph will highlight threads that are blocked or overutilized.

Now, since we don’t have any previous Thread State Trace graph, we can re-run the instruments and do the exact same scenario again. Once we stop the recording, Xcode will gather the graph informations and show it to the Instruments graph, ready for us to fix.

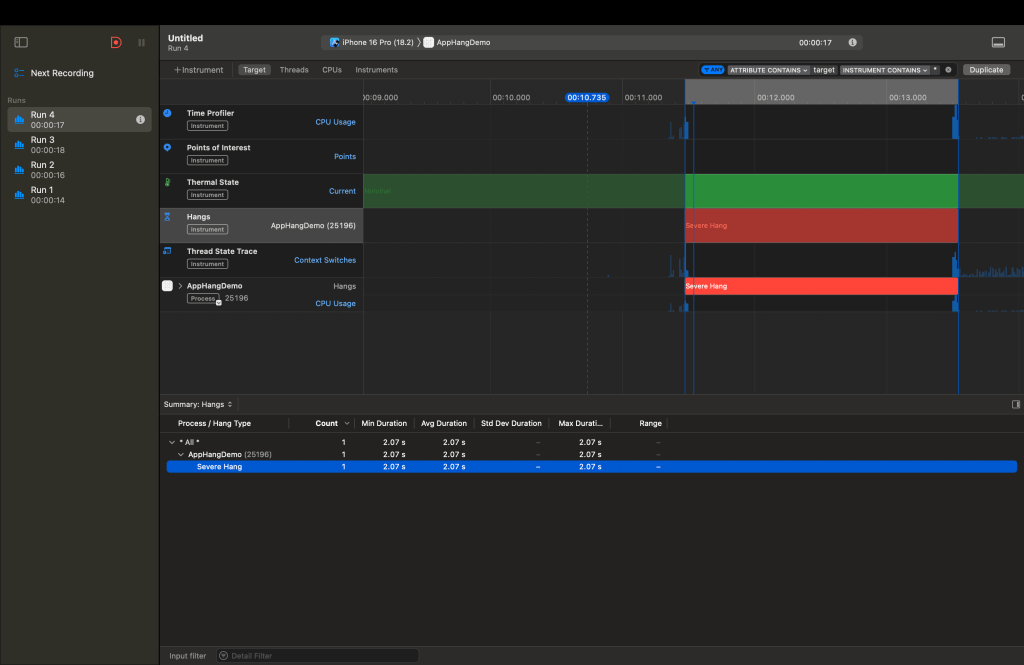
By analyzing these traces, you can pinpoint where the main thread is blocked.
How to Fix the UI Hang
The hang occurs because heavy computations are executed on the main thread, which blocks UI updates and prevents user interactions. By using the Thread State Trace, and a bit of investigation, selecting the correct chunk of graph we want to investigate, we will ended up on the right method that might cause the hang, like shown in the image below :

The Instruments trace indicates that a severe hang occurred, as highlighted in the “Hangs” graph. During this time, the main thread was blocked, preventing it from processing user interactions or updating the UI. The call stack points to the ContentView.loadData() method as the origin of the hang, where heavy computation or a delay was executed directly on the main thread, rendering the app unresponsive.
One critical detail is the presence of a 2-seconds hang message in the timeline, which corresponds to the simulated delay (Thread.sleep(forTimeInterval: 2)) inside the loadData function. This confirms that this function is responsible for the issue. Additionally, operations like mapping over a large dataset were not offloaded to a background thread, further contributing to the blockage of the main thread.
This scenario underscores the importance of moving computationally expensive tasks to a background thread to ensure smooth UI updates and avoid severe hangs like this one.
For a quick demonstration and fix, using DispatchQueue is a simple and effective way to prove that the hang can be resolved. Here’s the updated loadData function:
private func loadData() {
isLoadingData = true
DispatchQueue.global(qos: .userInitiated).async {
// Perform heavy computation on a background thread
let largeData = (1...100_000).map { "Item \($0)" }
Thread.sleep(forTimeInterval: 2) // Simulate heavy computation
DispatchQueue.main.async {
// Update the UI on the main thread
self.data = largeData
self.isLoadingData = false
}
}
}
For modern and scalable solutions in real-world applications, you can leverage Swift concurrency to handle concurrency more effectively and ensure thread safety. These approaches provide cleaner syntax and better integration with Swift’s concurrency model.
Now run the app and hangs will not be detected either using Instruments, or using built in app hangs detection on iOS device.
Detecting Hangs in Complex Applications
In real-world apps, hangs may not be as easy to identify. Use the Thread State Trace in Instruments to find the exact parts of your code causing the issue. Look for tasks running on the main thread that consume significant CPU time and optimize or offload them.
Conclusion
Detecting and fixing UI hangs is crucial for maintaining a smooth user experience. Use tools like App Hangs Detection and Instruments to diagnose performance bottlenecks. Ensure that heavy computations are executed on background threads, and always dispatch UI updates to the main thread.
By adopting these practices, you can build responsive and efficient iOS applications.
